We Continue to Lift Bitcoin in Sweden!
Nov 26, 2025
November may have seemed quiet on the surface, but behind the scenes we've laid the groundwork for important steps forward. Here at BTCX, we're looking forward to 2026! What we can say is that our focus remains where it has always been: strengthening the Bitcoin ecosystem, driving dialogue with decision-makers and continuing to develop products and services that make Bitcoin even simpler, safer and more accessible.

Goobit Group AB launches BTCX Bitcoin Treasury Strategy
Aug 4, 2025
Goobit Group AB (NGM: BTCX) ("Goobit" or “BTCX”) announces that it has launched a long-term Bitcoin Treasury Strategy. The first round is closed. The second round starts soon, and the goal is to hold as many bitcoins as possible on the balance sheet.

BTCHEL 2025 – The Biggest Bitcoin Celebration in the Nordics Is Coming!
Jul 24, 2025
On August 15–16, 2025, the Bitcoin community will gather in Helsinki for BTCHEL – or should we say BTCX-HEL) the very first large-scale Bitcoin conference ever held in Finland. Naturally, we at BTCX will be there, and we hope you’ll join what promises to be the most exciting event of the year for anyone who believes in a freer, more decentralized future.

BTCX Women & Bitcoin Podcast: Freedom, Identity, and Balance in a New World – with Fati Hakim
Jul 24, 2025
In our latest podcast episode, we meet Fati Hakim, CEO and co-founder of First Block, a Web3 and blockchain consultancy grounded in decentralization, innovation, and human freedom.
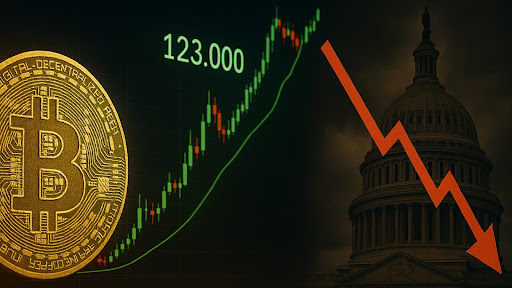
Bitcoin Hits New All-Time High Above $120,000 – As the Foundations of the U.S. Economy Begin to Tremble
Jul 24, 2025
On Monday, July 14, 2025, Bitcoin once again made history. For the first time ever, the price surpassed $120,000, peaking above $123,000 during a 24-hour period filled with activity, optimism — and a touch of nervousness across the crypto world. But the real story isn’t just the number — it’s what’s happening around the world right now.

From Life Chaos to the Stage: Bitcoin for Busy Women at Nordic Blockchain Conference
Jun 24, 2025
What an incredible few days! On June 18–19, the voices of the future gathered at Nordic Blockchain Conference 2025 at Epicenter in Stockholm – and of course, we were there!

Bitcoin Takes the Stage in Almedalen – BTCX Opens the Conversation on the Future of Money
Jun 24, 2025
It’s time to bring Bitcoin into the political conversation — for real. And Almedalen Week 2025 is the perfect opportunity. BTCX’s founder and CEO, Christian Ander, is participating this week in two key panel discussions focused on the future of money, competition in the financial market, and — of course — how Bitcoin can help build a more open, fair, and inclusive economy.
Get Started Now!
You can buy and sell bitcoin as soon as your information is verified!
Create an account

